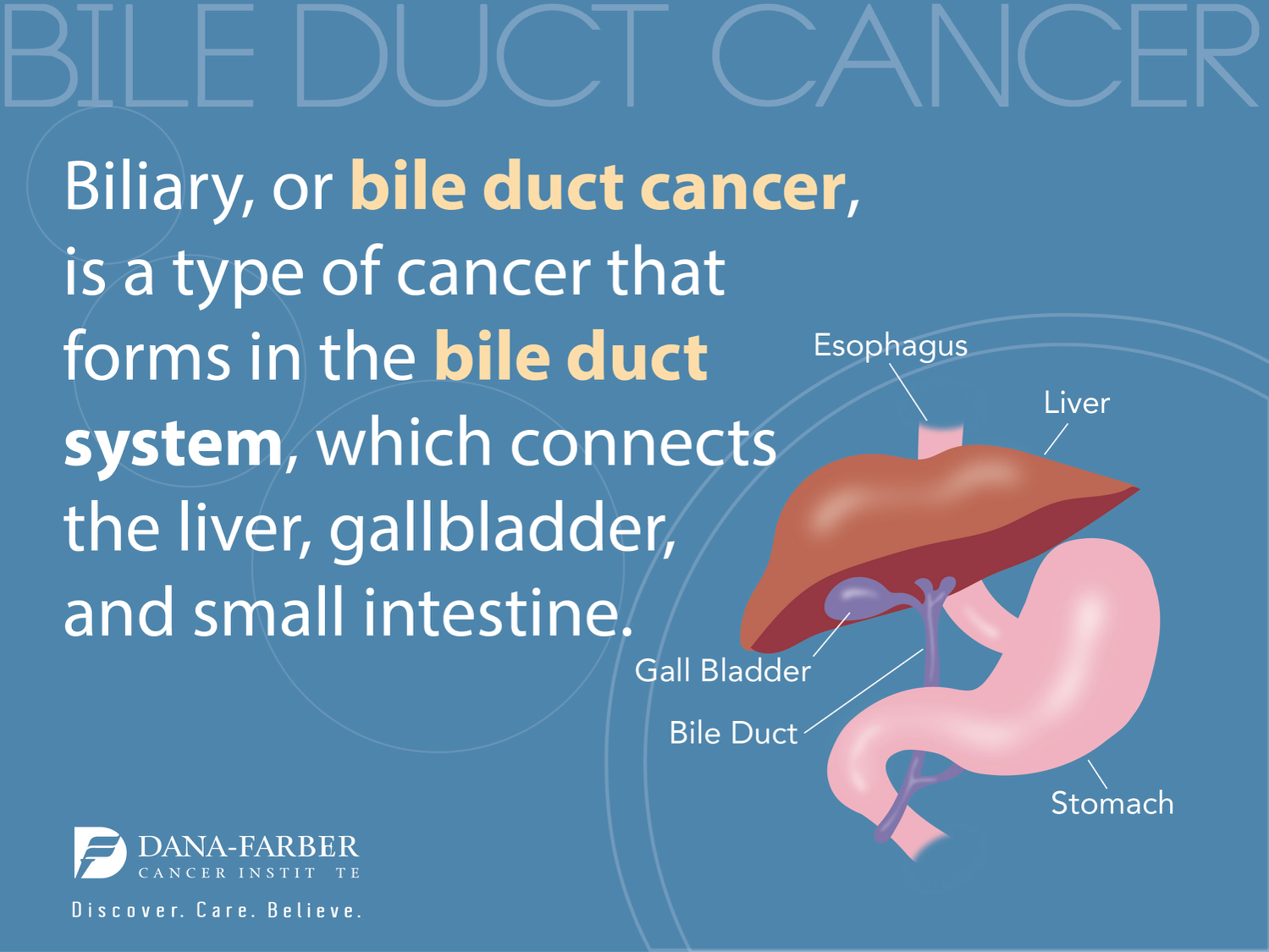
U.S. health innovation has become a cornerstone of modern medical advancements, setting a benchmark that countries around the globe aspire to achieve. Rooted in a rich history that was significantly shaped by the exigencies of World War II, the American approach to health innovation started with government-supported biomedical research that led to breakthroughs like the mass production of penicillin. Public-private partnerships have fueled further innovation, ensuring a steady flow of scientific research funding that propels the industry forward. As the landscape continues to evolve, the collaboration between academia, industry, and government fosters a dynamic environment where novel medical solutions are consistently developed. The historical impact of WWII not only galvanized these partnerships but also established a foundation upon which the current health innovation ecosystem stands.
In discussing advancements in healthcare, the phrase ‘American medical progress’ often comes to mind, reflecting the robust interconnections between various sectors. The evolution of this system, heavily influenced by past global conflicts, reveals how strategic partnerships between public institutions and private enterprises can drive groundbreaking discoveries. Scientific funding in the United States has cultivated an environment ripe for innovation, granting researchers the resources needed to explore new medical frontiers. From the early days of antibiotic production during wartime to today’s cutting-edge therapies, the journey of U.S. health innovation illustrates a narrative of resilience and creativity in tackling complex health challenges. Therefore, we continue to witness a remarkable trajectory in medical breakthroughs that echo the foundational strategies established decades ago.
The Evolution of U.S. Health Innovation
The U.S. has a long-standing tradition of health innovation that can be traced back to pivotal moments in history, particularly during World War II. The urgent need for effective medical solutions led to significant governmental investments in biomedical research. This era saw the mass production of penicillin, a groundbreaking advancement that transformed healthcare not only for military personnel but also for civilians. With public-private partnerships flourishing, universities and private firms began to collaborate extensively, leading to a system of research and development that has become the envy of nations worldwide.
Post-World War II, this momentum in health innovation continued to grow as the partnership between federal entities like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and academic institutions solidified. Funding for scientific research increased, creating a ripple effect that boosted the biopharmaceutical industry. This partnership paradigm paved the way for continuous medical advancements, ensuring the U.S. retained its global leadership in health innovation through further breakthroughs in drug discovery and therapies.
Public-Private Partnerships: The Backbone of Innovation
Public-private partnerships have become instrumental in driving innovation across multiple sectors, especially in biomedical research. The collaboration between government agencies and the private sector allows for the pooling of resources, expertise, and knowledge, leading to breakthroughs that neither party could achieve alone. For instance, the successful development and mass production of antibiotics during World War II exemplified how federal support could catalyze private industry advancements, solving urgent military health crises through innovative solutions.
As these partnerships evolved over the decades, they focused on various issues ranging from infectious diseases to chronic conditions. The historical impact of WWII on shaping these relationships cannot be understated; it was during this time that the framework for modern R&D funding was established. This cooperative model has since grown into a robust ecosystem that supports scientific research funding, resulting in a competitive landscape for medical advancements that benefits all.
Federal Funding Trends and Their Impact on Research
The dynamics of federal funding have played a crucial role in shaping the landscape of biomedical research in the U.S. Initially, the government’s significant investments were motivated by wartime needs but have since evolved into a broader strategy aimed at enhancing public health outcomes. As researchers depend heavily on scientific research funding from agencies like the NIH, any proposed cuts or changes could have dire consequences for innovation. For example, recent discussions around capping reimbursements for indirect research costs raise concerns about the sustainability of research infrastructure.
This trend of scrutinizing federal funding not only impacts current research projects but also threatens the future of groundbreaking advancements in medicine. Effective partnerships among stakeholders in the public and private sectors are crucial in maintaining robust funding mechanisms. The challenge lies in balancing fiscal responsibility while ensuring that the innovative machine that has provided so many medical breakthroughs continues to operate effectively.
Biomedical Research Funding: A Vital Component
Biomedical research funding is at the heart of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, driving essential advancements in medicine and public health. The collaborative efforts across universities, private firms, and governmental organizations have fostered an environment ripe for innovation. With ongoing research into chronic and infectious diseases, the capital that flows into this sector is not merely an investment in the economy; it is an investment in the health and well-being of the population.
The rapid pace of medical advancements we have witnessed over the last few decades, including groundbreaking treatments and technologies, can be directly attributed to the strong commitment to funding in biomedical research. However, the current landscape poses a risk, as increasing budget restrictions could undermine the very foundation that supports this research. It is crucial that stakeholders advocate for stable funding to ensure that the pipeline for discovery and innovation remains open and productive.
Lessons from WWII: Innovation for Health
The historical impact of World War II on U.S. health innovation provides valuable lessons on how to respond to urgent health crises. The collaborative approach adopted during the war not only led to significant advancements in medical technology but also established a model that continues to influence public health policy today. As scientists worked relentlessly to address the challenges posed by infectious diseases that plagued soldiers, the pressing need for effective solutions paved the way for substantial medical breakthroughs.
By investing in biomedical research during periods of crisis, the U.S. showcased how targeted funding and cooperative efforts can yield remarkable health outcomes. The strategies developed during this time are still relevant today, especially in addressing contemporary health threats like pandemics or antibiotic resistance. The lessons learned underscore the importance of readiness and cooperation between government and private sectors in fostering an innovative environment capable of tackling future health challenges.
The Role of Universities in Medical Advancements
Universities have always been at the forefront of medical advancements, serving as a crucible for innovation and scientific discovery. With their focus on education and research, institutions of higher learning play a crucial role in training the next generation of scientists and researchers. The collaboration between universities and federal funding agencies has enabled academic institutions to conduct vital biomedical research that addresses pressing health challenges.
Additionally, the historical context reveals that universities significantly contributed to the U.S. health innovation ecosystem during WWII. By mobilizing their resources and expertise, academic institutions helped develop new technologies and treatments, demonstrating their potential to catalyze change in the health sector. This synergy between academic ambition and federal support has shaped a thriving research environment that continues to push the envelope on medical breakthroughs today.
Challenges Facing the U.S. Health Innovation Ecosystem
Despite the undeniable successes of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, it faces several challenges that may impede future advancements. One of the significant issues is the funding landscape, which has seen increasing scrutiny and potential cuts from federal sources. As research funding becomes more restricted, the capacity for ongoing biomedical research may dwindle, leading to fewer breakthroughs and innovations in medicine. Additionally, there are concerns about aging infrastructure and the need for modernized facilities to support cutting-edge research.
Moreover, disparities in funding between different research sectors can create inefficiencies and slow the pace of innovation. Ensuring equitable access to funding sources is crucial for fostering a diverse and vibrant research landscape. As the ecosystem evolves, it is imperative that both public and private stakeholders work together to address these challenges and ensure continued growth and innovation in health research.
How Federal Policies Shape Innovation
Federal policies have a profound impact on the innovation landscape in biomedical research. The decisions made by lawmakers regarding funding priorities, regulatory frameworks, and research guidelines directly influence the direction of scientific inquiry and development. Recent discussions on modifying funding structures, particularly regarding indirect research costs, have raised concerns among researchers about the potential ramifications for future innovations.
Policies that support collaboration between government entities, private firms, and universities not only enhance the effectiveness of biomedical research but also spur economic growth. By establishing clear regulatory pathways that encourage innovation, policymakers can create an environment conducive to research and development, ultimately leading to significant advancements in health and technology.
The Future of U.S. Innovation: Ensuring Continuity
Looking ahead, the continuity of the U.S. health innovation ecosystem hinges on maintaining robust partnerships among federal entities, academic institutions, and private industries. The collaborative legacy that began during World War II must be reinforced to adapt to the changing landscape of healthcare needs. As new health crises emerge and technologies evolve, the ability to pivot quickly will be crucial for maintaining the U.S.’s status as a global leader in biomedical innovation.
Furthermore, investment in workforce development and training is essential for sustaining innovation. As the landscape of scientific inquiry continues to change, attracting and retaining talent in the fields of biomedicine and technology will be paramount. By fostering an environment that values education, collaboration, and open communication, the U.S. can continue to thrive as a beacon of health innovation, ensuring that its contributions positively impact global health for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did U.S. health innovation begin during World War II?
U.S. health innovation was significantly propelled by government-supported biomedical research during World War II. This era marked the initiation of public-private partnerships, where civilian scientists collaborated with the military to develop new medical technologies, including the mass production of penicillin, which drastically improved soldier health and laid the groundwork for future medical advancements.
What role do public-private partnerships play in U.S. health innovation?
Public-private partnerships are vital in the U.S. health innovation ecosystem, fostering collaboration between government, academia, and the pharmaceutical industry. These partnerships have been instrumental in securing scientific research funding that spurs medical advancements and enhances the nation’s global competitiveness in biomedical research.
How has historical impact of WWII shaped today’s U.S. health innovation system?
The historical impact of World War II is profound in shaping today’s U.S. health innovation system. The wartime urgency led to significant advancements in biomedical research, including the establishment of the National Institutes of Health, which now plays a crucial role in funding scientific research and supporting the development of new therapies.
What were the main breakthroughs in biomedical research during WWII?
During World War II, significant breakthroughs in biomedical research included the mass production of penicillin and innovations in disease prevention and treatment. These advancements resulted from extensive research funded by the government through agencies like the Office of Scientific Research and Development, which directed projects aimed at improving soldier health.
Why is scientific research funding important for U.S. health innovation?
Scientific research funding is essential for U.S. health innovation as it supports the discovery and development of new medical technologies and treatments. Federal investment, particularly through partnerships with universities and private sectors, enables researchers to explore advanced biomedical studies that can lead to significant medical advancements.
What challenges does the U.S. health innovation system face today?
Today, the U.S. health innovation system faces challenges such as potential cuts to scientific research funding, particularly from federal sources like the National Institutes of Health. These funding changes could disrupt the collaborative public-private partnerships that have historically driven biomedical research and innovation.
How did the U.S. establish a leading role in global health innovation?
The U.S. established a leading role in global health innovation through a combination of robust government support for biomedical research, strong academic institutions, and dynamic public-private partnerships. This system has fostered groundbreaking advancements in medicine and technology, making the U.S. health innovation ecosystem the envy of the world.
What contributions did wartime medical research have on post-war biomedical advancements in the U.S.?
Wartime medical research contributed significantly to post-war biomedical advancements by laying the foundation for modern drug development processes and creating new research methodologies. The infrastructure and scientific expertise developed during WWII enabled a surge in innovations that defined the subsequent golden age of biomedical breakthroughs.
How did the introduction of indirect cost funding impact U.S. biomedical research?
The introduction of indirect cost funding during WWII was crucial as it incentivized universities and private firms to engage in military R&D projects. By compensating for overhead expenses, the U.S. government encouraged participation, fostering a collaborative environment that paved the way for significant advancements in biomedical research.
What future prospects are there for U.S. health innovation?
The future prospects for U.S. health innovation remain strong, driven by ongoing public-private partnerships and continued federal support for biomedical research. With a commitment to maintaining robust scientific research funding, the U.S. can further enhance its position as a leader in global health innovation, ensuring continued breakthroughs in medical technology and treatments.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. health innovation ecosystem began during World War II with government-supported research that led to significant medical breakthroughs. |
| Mass production of Penicillin was one of the most significant achievements, dramatically reducing military hospital admissions for infectious diseases. |
| The federal government’s role has expanded since WWII, leading to partnerships between academia and industry that drive ongoing biomedical advancements. |
| Programs such as the OSRD were created to fund and coordinate wartime medical research, which set the foundation for modern biomedical innovation. |
| The partnership has fostered an environment where new drug development was possible, benefiting both military and civilian health over the decades. |
| Today, the U.S. continues to lead in health innovation, with extensive collaborations that enhance research and development efforts across various sectors. |
Summary
U.S. health innovation is the result of a robust ecosystem built over decades, starting from critical wartime advancements. This partnership between the federal government, academia, and the private sector has catalyzed extraordinary progress in medical research and technology, laying the groundwork for a system that not only addresses national defense but also elevates public health standards. The U.S. stands as a global leader in health innovation, fostering continued advancements that improve the quality of life worldwide.