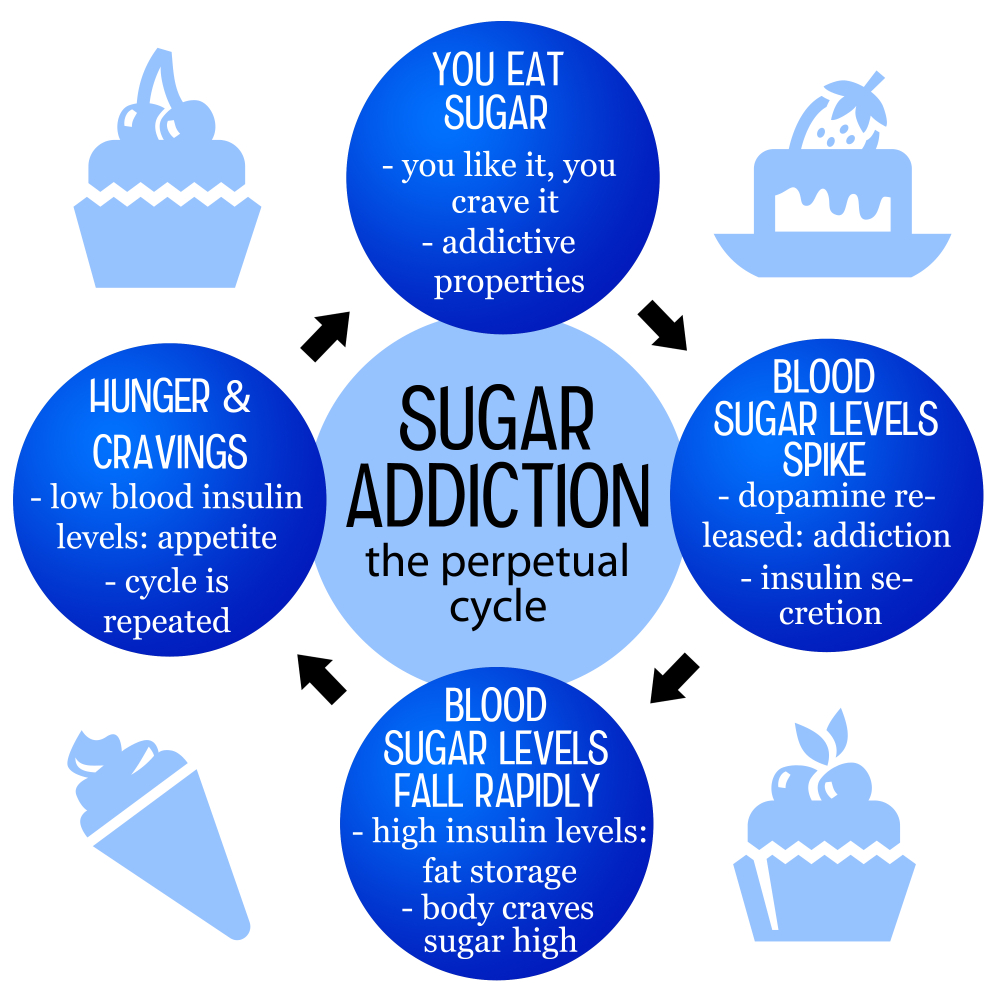
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked heated debates among nutritionists and health experts for years. While sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, research shows it can trigger intense cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The alarming truth is that our modern diet bombards us with processed foods high in added sugar, amplifying these cravings and leading to unhealthy habits. Understanding the health effects of sugar and the prevalence of sugar addiction is essential for making informed dietary choices and reducing the risks associated with excessive intake.
The concept of sugar dependency often arises in discussions about dietary habits and their psychological impacts. Many individuals find themselves grappling with overwhelming desires for sweet treats, a phenomenon that can be linked to the consumption of processed foods laden with added sugars. Such cravings can lead to what feels like a cycle of indulgence and regret, making it difficult to adopt healthier eating patterns. As we explore the nuances of this topic, we must consider how sugar influences our well-being and mental state, warranting a closer look at our daily sugar intake and its potential effects on our health.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question of whether sugar is addictive remains a contentious topic among nutrition experts. While studies indicate that high sugar intake can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, sugar does not meet the clinical criteria classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, the feelings of withdrawal when cutting out ultra-processed foods rich in added sugars can resemble those associated with substance addiction. This suggests that for some individuals, the dependence on sugary foods can lead to negative health effects, including mood swings and anxiety.
It’s pivotal to acknowledge that sugar itself is not entirely bad—our bodies require it for energy. However, the problem arises when we consume it in excessive amounts through processed foods. The average American diet is flooded with added sugars, often hidden in items marketed as healthy. This perpetual cycle of sugar craving ties into the convenience and palatability of ultra-processed foods, making it challenging to consume sugar in moderation. Understanding this aspect helps demystify the relationship many have with sugar and can guide healthier dietary choices.
The Health Effects of Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption has profound health implications. The primary concern lies in added sugars often found in soft drinks, candies, and snacks, leading to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Monitoring intake can be difficult when many processed foods contain sugars that contribute to daily limits without our awareness. The American Heart Association recommends stringent limits on added sugar intake, and consistently surpassing these limits can severely affect overall health.
Moreover, the health effects of sugar extend beyond mere weight gain. High sugar diets can elevate triglycerides, lower good cholesterol (HDL), and result in insulin resistance. These factors can predispose individuals to metabolic syndrome, a precursor to many chronic illnesses. By becoming mindful of the amount of sugar consumed daily and opting for whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can mitigate these health risks and promote overall wellness.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Managing sugar cravings can be a daunting task, especially for those used to a diet high in added sugars. One effective strategy is to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than eliminating it abruptly, as this can lead to heightened cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Instead, focusing on nutrient-dense foods like fruits and vegetables can naturally satisfy sweet cravings while providing essential nutrients that aid in overall health.
Additionally, incorporating balanced meals that combine proteins, fats, and fibers can help regulate blood sugar levels and minimize sudden spikes followed by crashes that often lead to sugar cravings. Keeping hydrated and ensuring adequate sleep also play crucial roles in managing cravings, as dehydration and fatigue can sometimes be misinterpreted as hunger. By integrating these habits into daily life, individuals can reduce their dependence on sugar and promote healthier eating patterns.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Addiction
Processed foods are often culprits in the sugar addiction debate. Many commercially available snacks and meals contain high levels of added sugars that enhance flavor but contribute to addictive eating patterns. Their accessibility and convenience make them attractive choices, often leading individuals to consume these high-sugar alternatives repeatedly. These foods can create a cycle of cravings driven by the rush of taste, making healthy eating choices less appealing.
Furthermore, the marketing techniques employed by companies often mislead consumers into believing these processed snacks are healthier than they are. Sugar-laden items marketed as ‘low-fat’ or ‘high in fiber’ may still contain excessive added sugar, contributing to poor dietary habits. It’s essential to read food labels carefully to avoid hidden sugars and make more informed choices, as this awareness is crucial in breaking the dependency on processed foods.
The Importance of Moderate Sugar Intake
While sugar is often vilified in discussions about diet and health, it’s important to note that moderate sugar intake is not inherently harmful. In fact, sugars found in whole foods like fruits and dairy are part of a balanced diet and provide energy and essential nutrients. The key lies in distinguishing between naturally occurring sugars and those added to processed foods. Emphasizing moderation can help demystify sugar’s role in nutrition and reduce negative perceptions surrounding its consumption.
For those looking to manage their sugar intake, focusing on portion control and being mindful of sugar content in foods can help cultivate a healthier relationship with sweetness. By ensuring that added sugars are limited to occasional treats, it’s possible to enjoy the pleasures of sugary treats without their adverse effects on health. Creating a sustainable, balanced approach to sugar can lead to long-term well-being and satisfaction.
The Psychological Impact of Sugar Consumption
The psychological effects of sugar consumption are closely tied to emotional well-being and can influence cravings and overall mood. Many people turn to sugary snacks for comfort or a quick energy boost during stressful times, perpetuating a cycle where sugar intake becomes a coping mechanism. This reliance on sugar can lead to emotional eating patterns, making it difficult to break free from cravings.
Additionally, understanding the emotional triggers behind sugar consumption can empower individuals to seek healthier alternatives. For instance, replacing sugary snacks with fruits or nuts can satisfy cravings while providing nutritional benefits without the added sugars. Addressing emotional needs through methods such as mindfulness or healthy cooking can also create a more positive framework for managing cravings and achieving a balanced relationship with food.
Identifying Added Sugar in Foods
Identifying added sugars in foods is crucial for anyone aiming to manage their sugar intake effectively. Many packaged foods contain hidden sugars that are not immediately obvious from their marketing labels. To navigate this, individuals should familiarize themselves with common types of added sugars, such as sucrose, high fructose corn syrup, and various syrups.
Reading ingredient lists and seeking items with lower sugar content is vital. Ingredients are listed in descending order by weight, meaning that if sugar appears at the top of the list, the product is likely high in added sugar. By making it a habit to check food labels, individuals can take proactive steps toward reducing their sugar consumption and improving their dietary habits.
Building Healthy Eating Habits
Building healthy eating habits is essential for long-term well-being and can significantly reduce sugar cravings. This involves not only making healthier food choices but also developing a mindful eating approach that focuses on enjoyment and satisfaction. Eating slowly and savoring meals can enhance overall satisfaction, potentially leading to reduced cravings for sugary or processed foods.
Additionally, planning meals and snacks can foster better eating habits by ensuring that nutritious options are always within reach. Incorporating a variety of flavors and textures can keep meals interesting and satisfying without the need for significant sugar content. By nurturing these habits, individuals can create a more balanced diet that lessens the appeal of high-sugar snacks and supports overall health.
The Future of Sugar Research
The future of sugar research continues to evolve as more studies emerge revealing the complexities of sugar consumption and its impacts on health. Ongoing research is focusing not only on the physical effects of sugar but also on psychological dependencies and societal influences surrounding sugar intake. This holistic approach may provide insights into better dietary recommendations and effective strategies to combat sugar addiction.
As the discourse around sugar persists, it is imperative to remain open to new findings that challenge existing beliefs. Understanding sugar’s role from both health and sociocultural perspectives can inform public health initiatives, educational programs, and personal strategies to improve wellness in a society where sugar is ubiquitous. Engaging with the latest research will empower individuals to make informed decisions about their sugar consumption and overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive in the same way as nicotine or alcohol?
While sugar can trigger cravings similar to addictive substances like nicotine and alcohol, it is not classified as an addictive drug according to clinical standards. Sugar does influence compulsive eating behaviors, especially due to its presence in processed foods, but the withdrawal symptoms are generally less severe than those associated with true addictions.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to cravings and habitual consumption of high-sugar processed foods, which may contribute to weight gain, increased risk of chronic diseases, and negatively impact mental health. Reducing added sugar intake gradually is recommended to minimize these health risks.
How does sugar addiction relate to processed foods?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, making them more palatable and increasing the likelihood of cravings. This can create a cycle of habitual consumption, reinforcing the desire for sugary foods and potentially leading to sugar addiction.
What causes sugar cravings and how can they be managed?
Sugar cravings arise from frequent consumption of sugary and processed foods, which can lead to physiological dependence. To manage sugar cravings, focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, reduce sugar intake gradually, and stay hydrated.
Are there withdrawal symptoms associated with sugar addiction?
Yes, individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they reduce sugar intake, including headaches, anxiety, and mood swings. These symptoms are typically more mild compared to those associated with substances like nicotine or alcohol.
Is it possible to eliminate sugar completely from my diet?
While it is possible to eliminate added sugars found in processed foods, sugar naturally occurs in many healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy. A balanced approach is advisable, focusing on moderation rather than complete elimination.
What is the recommended daily intake of added sugar to avoid sugar addiction?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children, to minimize health risks associated with sugar addiction.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sugar Addiction Debate | While sugar can stimulate cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not officially classified as addictive based on clinical criteria. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | Foods high in sugar, fats, and sodium increase cravings and consumption habits, leading to withdrawal-like symptoms when they’re eliminated. |
| Need for Sugar | Unlike addictive substances that can be completely eliminated, we need some sugar in our diets for survival, as it is present in many healthy foods. |
| Consumption Recommendations | The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of sugar daily, surpassing recommendations of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
| Gradual Reduction | It’s advised to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than stopping abruptly, which could lead to negative effects. |
| Positive Aspects | Sugar enhances flavor and pleasure in food, making a complete elimination from diet unproductive. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among experts. While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine, it does not meet the strict clinical definitions of addiction. Therefore, while excessive sugar consumption can lead to negative health outcomes, it is essential to recognize that sugar also serves a vital role in our diets. Moderate sugar intake can enhance the taste of foods and contribute positively to our diets when consumed responsibly.