Social interaction needs are increasingly recognized as essential components of human health and well-being. Just as we require food and water to survive, our brains are wired to seek out and maintain connections with others. Recent research delves into the neurological basis of social connection, revealing how the brain governs our instinctual drive for companionship. The significance of social contact has been highlighted in several studies, particularly in light of the health effects of loneliness which have emerged as a pressing public health concern. Understanding these social interaction needs not only sheds light on the complexities of human behavior but also presents vital implications for addressing issues related to social isolation.
When we think about the fundamental requirements for a fulfilling life, it’s crucial to consider how our interactions with others shape our mental and emotional landscapes. Terms like social connectivity and companionship encapsulate the essence of what we need to thrive as humans. Emerging research into the neuroscience of social engagement emphasizes the importance of relationships and how they impact our psychological health. From the dynamics of loneliness to the bonding experiences that define our communities, the ways we connect profoundly influence our overall quality of life. By examining these social connection essentials, we can better appreciate their role in fostering a sense of belonging and emotional well-being.
The Neurological Basis of Social Connection
Research has increasingly underscored the neurological basis of social connections, highlighting the brain’s architecture that prioritizes relational needs. Recent studies have identified critical neural circuits in the hypothalamus, a region traditionally associated with basic survival needs like hunger and thirst. By mapping these circuits, scientists have revealed that our instinctive drive for social interaction may share similarities with other fundamental biological urges. This groundbreaking research not only emphasizes the importance of social contacts but also elucidates how these interactions are intricately wired into our neurological frameworks.
The study conducted by Liu’s team meticulously examined the neural activities during both social deprivation and reunion phases in mice, showcasing the brain’s responsive systems to social interactions. When isolated, the heightened neural activities signal an underlying need for companionship, drawing parallels between loneliness and physical deprivation. This suggests that the brain encodes social needs similarly to how it responds to hunger, establishing a profound understanding of why fulfilling social interactions is crucial for overall health.
The Importance of Social Contact
The significance of social contact extends beyond mere companionship; it is critical for mental and emotional well-being. According to health professionals, engaging in social interactions is not just a luxury but a necessity that greatly influences our health. Individuals lacking meaningful social connections are at risk for negative health outcomes, ranging from mental health disorders like depression and anxiety to physical complications. By recognizing social contact as a basic human need, we can better address the growing crises of loneliness and isolation that plague societies worldwide.
Health officials and researchers alike emphasize that understanding the dynamics of social contact is paramount, especially in the context of increasing social isolation. The parallels drawn between social needs and physiological needs suggest that fulfilling these interactions is essential for achieving optimal health. As ongoing studies continue to explore how social bonds contribute to our overall well-being, it becomes evident that fostering connections and communities is crucial in combating the detrimental effects of loneliness.
Health Effects of Loneliness
The health effects of loneliness are profound and far-reaching, influencing not only mental health but also physical well-being. Scientific evidence indicates that prolonged loneliness can lead to various health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, weakened immune responses, and even cognitive declines. Health professionals are now urging individuals to prioritize social interactions alongside their physical health routines, emphasizing that neglecting these relationships can be just as harmful as unhealthy eating or lack of exercise.
Moreover, the concept of social isolation has emerged as a pressing public health concern. The U.S. Surgeon General’s acknowledgment of this issue in 2023 highlights the urgent need for community and societal strategies to foster social connections among individuals of all ages. As we navigate an increasingly digital world, understanding the risks associated with loneliness becomes essential to mitigating its impact on our health.
Social Isolation Research and Its Implications
Social isolation research sheds light on the alarming trends in human connection and community engagement. With studies indicating that the prevalence of loneliness has surged in recent years, understanding its implications is critical for public health. Researchers are focusing not only on the effects of social isolation on mental health but also on its physiological impacts, revealing that those suffering from loneliness show significantly higher levels of stress and anxiety.
Additionally, research findings can guide interventions and policies aimed at alleviating loneliness. For instance, initiatives designed to enhance community interactions and promote social programs could have far-reaching benefits in boosting mental health resilience. By continuing to examine the multifaceted nature of isolation, we can explore innovative solutions that encourage active social engagement and foster supportive environments.
The Brain’s Role in Social Behavior
Understanding the brain’s role in social behavior provides crucial insights into why social connections are essential for our well-being. The dynamic brain circuits involved in social interaction not only influence how we relate to others but also have substantial implications for mental health disorders. Recognizing that specific neural pathways govern the desire for companionship offers a new perspective on treating conditions like anxiety and depression, where social needs are often unmet.
Through ongoing studies, scientists are gaining clarity about the interplay between the brain and social behavior. For example, by examining the activity of social neurons in the hypothalamus, researchers can identify how various experiences—both fulfilling and isolating—impact our psychological state. This understanding underscores the imperative to foster social environments that support positive interactions as a means of improving mental health outcomes.
Exploring Social Interaction Needs in Modern Society
In contemporary society, it is crucial to explore our fundamental needs for social interaction and how they are being met. With the rise of digital communication tools, face-to-face conversations have decreased, leading to an increase in feelings of isolation. This shift calls for a critical evaluation of our social interaction behaviors and the importance of nurturing in-person connections as a counterbalance to technological engagement.
Addressing social interaction needs is not just about enhancing personal relationships; it also has broader societal implications. By prioritizing social engagement and fostering environments that allow for meaningful interactions, communities can combat loneliness. In doing so, they enhance collective mental health, leading to a more interconnected and resilient society capable of thriving amid modern challenges.
The Psychological Foundations of Social Bonds
Delving into the psychological foundations of social bonds illuminates the essential nature of human relationships. The strong correlation between social connections and psychological health is underscored by recent research, which indicates that feeling connected to others significantly enhances overall life satisfaction. The psychological benefits of belonging are so profound that they can serve as protective factors against various mental health issues.
Moreover, understanding how social bonds function psychologically invites new methodologies in treatment and community building. Therapists are increasingly incorporating social interaction frameworks into therapy, encouraging clients to engage more deeply with their communities. The transformative power of supportive relationships not only nourishes the individual psyche but also fosters healthier, more vibrant communities.
Interactions of Social Behavior and Biological Needs
The interactions of social behavior with biological needs present a fascinating area of study. As highlighted by current research, our bodies and minds are not separate entities; they function integratively. The need for companionship can often mirror foundational biological urges such as hunger and thirst, indicating that fulfilling social interactions might be as essential as satisfying basic physical needs.
This integration suggests a holistic approach to health, wherein medical and psychological practices align. Such understandings can shape future health policies and therapeutic practices, promoting more comprehensive care that addresses both psychological and physical needs. A nuanced awareness of how social behavior interplays with biological imperatives marks a progressive shift in how we think about overall well-being.
Importance of Touch in Social Interactions
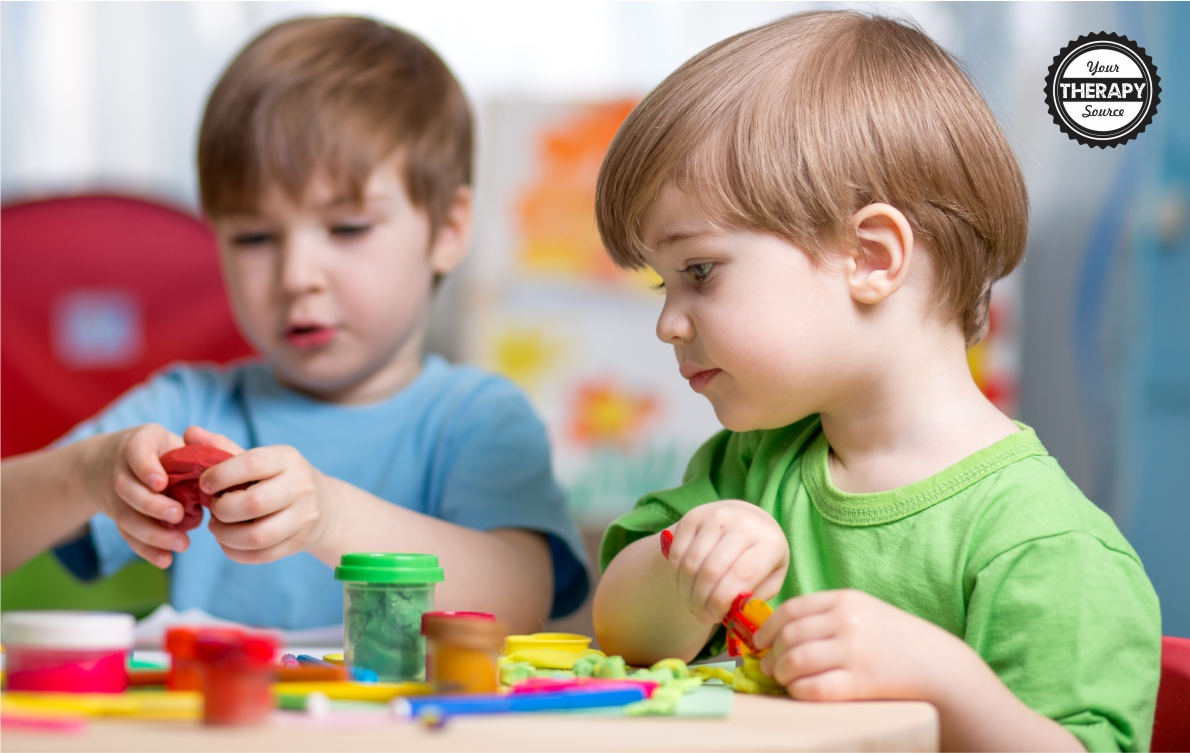
As highlighted in the research, the significance of touch in social interactions cannot be overstated. Touch is not only a language of connection but also a critical component for fulfilling our inherent social needs. The studies indicated that, much like mice gravitated towards a soft environment post-isolation, humans too thrive when touch is part of their social exchanges. This can encompass everything from casual greetings to deep interpersonal bonds.
In a world increasingly reliant on digital communication, the absence of physical touch can lead to a void in social fulfillment. As scientists explore the essential nature of touch, it also raises awareness regarding mental health challenges in today’s society, where nonverbal cues and physical presence are often diminished. Learning to prioritize and integrate touch into our interactions will be vital for enriching human connections and fostering emotional well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social connection and why is it important?
The neurological basis of social connection involves specific brain circuits that govern our instinctive need for social interaction, similar to basic needs like hunger and thirst. Research indicates that maintaining social contact is crucial for mental health, as the brain encodes social needs alongside physiological needs such as food and water, highlighting the importance of social contact for overall well-being.
How does social isolation affect mental health?
Studies show that social isolation can lead to serious health effects, including increased risks of mental illnesses like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. The lack of fulfilling social interactions disrupts the brain’s regulatory systems for social behaviors, making social isolation a significant public health concern.
What are the health effects of loneliness and social isolation?
Loneliness and social isolation have profound health effects, including increased risk of heart disease, cognitive decline, and mental health disorders. These issues stem from the brain’s strong wiring for social connection, suggesting that humans are hardwired to seek companionship and that prolonged isolation can lead to detrimental health outcomes.
What role does physical touch play in fulfilling social interaction needs?
Physical touch is a critical component of social interaction needs, as evidenced by research showing that individuals and animals alike prefer tactile experiences, such as hugging or handshakes, to fulfill their social needs. Touch enables the brain to process social stimuli, thus playing an essential role in maintaining healthy social bonds.
How does the brain regulate the need for social interaction?
The brain regulates the need for social interaction through neural circuits located in the hypothalamus, which are responsible for basic needs like food and water. These circuits activate during moments of social deprivation, indicating that the drive for social connection is akin to drives for basic physiological needs.
Why is social connection considered a fundamental human need?
Social connection is deemed a fundamental human need due to its critical role in mental and physical health. Research shows that just like food and water, social interactions are vital for a healthy life, as they help prevent feelings of loneliness and contribute to emotional well-being.
What insights can social isolation research provide about human behavior?
Social isolation research provides valuable insights into the fundamental biological and psychological motivations for social interaction. By understanding how the brain responds to social deprivation, we can better appreciate the essential nature of social bonds and their influence on mental health and relationships.
What have studies revealed about the effects of isolation on mice and its relation to humans?
Studies on mice, which demonstrate changes in social behavior after prolonged isolation, suggest that similar effects may occur in humans. This research indicates that physical proximity and tactile interactions are crucial for fulfilling social needs, reinforcing the idea that humans require real-life social connections to thrive.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection as a Basic Human Need | Health professionals now consider social contact as vital as food and shelter, highlighted by the U.S. Surgeon General recognizing social isolation as a major health concern in 2023. |
| Neurological Basis of Social Interaction | Research led by Ding Liu explores how the brain encodes the need for social interaction, focusing on the hypothalamus, the area responsible for basic needs like hunger and thirst. |
| Impacts of Isolation | Prolonged social isolation can shift preferences, making individuals dislike social behavior over time, illustrating the importance of physical touch for social fulfillment. |
| Touch and Social Behavior | Touch is a crucial element of social interaction, with implications for humans in a digital age where physical contact may be decreasing. |
| Study’s Broader Implications | Understanding the biological foundations of social needs can help address mental health issues and enhance social bonding. |
Summary
Social interaction needs are fundamental to our well-being, as demonstrated by research revealing their neurological foundations. As health professionals recognize the critical nature of social connections, it’s essential to explore how these interactions affect mental health and relationships. This understanding not only highlights the importance of companionship but also sheds light on the repercussions of social isolation, emphasizing that our biological makeup must include opportunities for meaningful social engagement in our daily lives.