CALEC surgery, an innovative advancement in ocular medicine, promises renewed hope for individuals suffering from severe cornea damage that was once deemed irreparable. This groundbreaking procedure utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, offering a sophisticated approach to cornea restoration by harnessing the healing power of one’s own stem cells. In clinical trials, CALEC surgery has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness, providing not only symptom relief but also the potential for improved vision in patients suffering from eye injuries and various limbal deficiencies. As eye injury treatment continues to evolve, the efficacy of this new stem cell therapy highlights the critical role of limbal epithelial cells in maintaining corneal health, fostering optimism for those affected by corneal diseases. By focusing on personalized healing solutions, CALEC surgery stands at the forefront of cornea damage treatment, heralding a new era in ophthalmic care.
Cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell (CALEC) technique is revolutionizing the landscape of eye treatment, specifically targeting cases of corneal impairment characterized by limbal stem cell deficiency. This advanced method takes healthy cells from a patient’s intact eye, enhancing their ability to regenerate damaged ocular surfaces. As a significant contributor to corneal restoration, CALEC defines a pioneering direction for addressing debilitating injuries to the eye that were previously challenging to manage. Leveraging innovations in stem cell therapy, this therapeutic intervention is poised to alter the course of eye injury treatment, showcasing the body’s ability to rejuvenate itself. Through meticulous research and clinical trials, CALEC underscores the profound potential of leveraging biological materials in restoring functional vision, marking a vital step forward in addressing one of the most pressing issues in ophthalmology.
Understanding CALEC Surgery: A Breakthrough in Eye Care
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell surgery, represents a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment of cornea damage. This innovative procedure involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye, which are then transformed into a cellular tissue graft to repair the cornea of an injured eye. The process not only addresses serious conditions that can lead to blindness but also signifies a massive leap forward in stem cell therapy applications within ophthalmology. As demonstrated in clinical trials led by Mass Eye and Ear, CALEC surgery has shown potential to restore the cornea’s surface with over 90% efficacy, thus providing hope to those previously considering their condition untreatable.
The significance of CALEC surgery extends beyond just its procedure; it offers a glimpse into the future of corneal restoration by utilizing limbal epithelial cells effectively. When the cornea suffers from intense injuries, traditional methods like corneal transplants become limited. The ability to regenerate these vital stem cells allows for not just healing but improving visual acuity, creating greater prospects for everyday functioning and quality of life for patients. As more studies unfold, CALEC surgery is poised to transform the landscape of eye injury treatments.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Treating Cornea Damage
Stem cell therapy has become a cornerstone in regenerative medicine, particularly in the treatment of eye diseases. In the case of cornea damage, cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) provide a revolutionary approach by addressing limbal stem cell deficiency, which is a significant barrier to effective treatment. This therapy functions by restoring the eye’s outermost layer, the cornea, through the transplantation of lab-grown stem cells derived from a healthy eye. Recent clinical trials have observed remarkable success rates, highlighting the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy in the context of ocular rehabilitation.
The importance of this method stems from its ability to treat conditions caused by limbal stem cell deficiency, like chemical burns or trauma. Patients suffering from severe cornea injuries often endure lifelong debilitating conditions; stem cell therapies like CALEC pave the way for healing damaged tissues that might otherwise be beyond repair. With ongoing research and clinical trials, the full potential of stem cell therapy in corneal restoration continues to unfold, encouraging further advancements in regenerative health solutions.
How CALEC Surgery Works: Process and Procedure
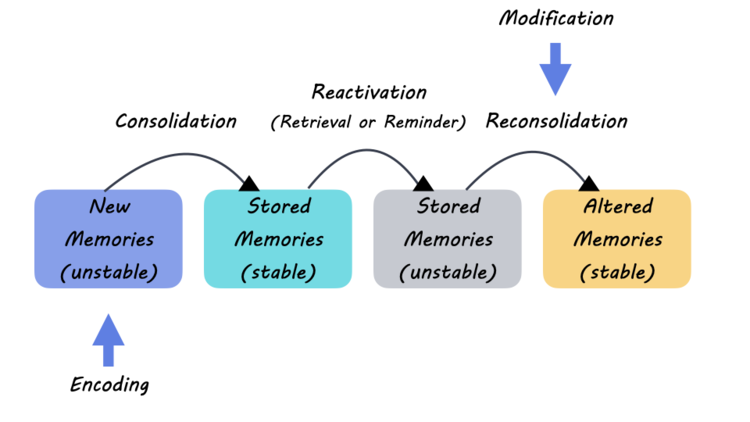
The CALEC surgery process is meticulously designed to restore the corneal surface using a patient’s own stem cells, ensuring a more personalized approach to treatment. Initially, a small biopsy is taken from the limbus of a healthy eye, where a wealth of limbal epithelial cells resides. These cells are then cultivated and expanded in a controlled lab environment over two to three weeks, ultimately creating a graft suitable for transplantation. This innovative approach not only enhances the healing process but also minimizes the risk of rejection, as the cells are autologous.
Once the graft is ready, the surgical phase involves transplanting these cultivated cells to the damaged eye. Post-operative evaluations have indicated that patients experience significant improvements in visual acuity, and many achieve restored corneal surfaces within months. The combination of advanced manufacturing processes and surgical expertise at institutions such as Mass Eye and Ear plays a pivotal role in the efficiency of CALEC surgery, making it a promising option for those with debilitating corneal injuries.
Clinical Trials: The Road to FDA Approval for CALEC
Clinical trials serve as a critical step in advancing CALEC surgery from the lab to mainstream clinical practice. The first study at Mass Eye and Ear not only demonstrated the safety of the procedure but also highlighted its effectiveness with a completion success rate approaching 93% over 18 months. Such achievements are pivotal for obtaining FDA approval, enabling wider access to this revolutionary treatment for patients afflicted by cornea damage who have limited options.
These trials, as the first human studies funded by the National Eye Institute, mark a significant milestone in stem cell research for ophthalmology. Future studies aim to expand participant groups and include diverse patient demographics, which could further solidify CALEC’s place as a leading method for treating cornea injuries. As the research continues, the hope is to streamline the regulatory process, ensuring that innovative treatments can reach those who need them most in a timely manner.
Emphasizing Safety in CALEC Procedures
Safety is paramount in any medical procedure, especially one involving stem cell therapy. In the clinical trials for CALEC surgery, patient safety was consistently monitored, with results indicating no serious adverse events in either the donor or recipient eyes. The procedure demonstrated a favorable safety profile, which is essential for building trust among potential patients and healthcare providers. Minor complications, such as a bacterial infection attributed to chronic contact lens use, were quickly resolved, further underscoring the procedure’s overall reliability and manageable risks.
The extensive follow-up periods in the trials allowed researchers to closely observe patient outcomes and adapt protocols as needed, ensuring that safety remains a focus throughout the CALEC process. As this treatment continues to develop, maintaining a commitment to patient safety will be integral to its acceptance in the broader medical community and its eventual transition to standard care for corneal injuries.
Future Prospects: Advancing CALEC Technology
The future of CALEC surgery looks promising, particularly with ongoing advancements in stem cell technology. Researchers are exploring ways to streamline the manufacturing process of limbal epithelial cells, potentially allowing for allogeneic grafts sourced from cadaveric donors. This progress could revolutionize how corneal damage is treated, making CALEC surgery accessible to a broader range of patients, including those with injuries to both eyes.
In addition to expanding treatment options, further investigations into CALEC could lead to enhancements in patient outcomes with the development of more robust and effective cellular grafts. Collaborative efforts among institutions like Mass Eye and Ear, Dana-Farber, and Boston Children’s Hospital are critical in this quest for innovation, ensuring that cutting-edge research translates into tangible benefits for eye care.
Patient Experiences: Insights From CALEC Trials
Patient feedback from the CALEC clinical trials has been overwhelmingly positive, showcasing not only the effectiveness of the treatment but also the compassionate care provided by the medical teams. Participants reported significant improvements in their quality of life, with many expressing relief from chronic pain and restoration of their vision. Such testimonials are crucial for understanding the real-world impact of CALEC surgery and reinforcing the need for further research.
Moreover, sharing patient experiences fosters awareness around corneal damage and the innovative methods being developed to combat it. As word spreads about CALEC surgery’s success, it may encourage others suffering from similar conditions to seek treatment, whether through clinical trials or once the procedure becomes widely available. Understanding these narratives humanizes the scientific endeavor, illustrating how advanced medical techniques can transform lives for the better.
The Science Behind Limbal Epithelial Cells and Corneal Health
Limbal epithelial cells play a vital role in maintaining the health of the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. These cells are essential for the regeneration of the cornea’s surface, ensuring clarity and protection against environmental damage. When these cells are depleted due to trauma, chemical burns, or diseases, patients may experience limbal stem cell deficiency, leading to severe visual impairments and pain. CALEC surgery addresses this critical issue by replenishing the supply of these necessary cells to restore corneal function.
The intricate relationship between limbal epithelial cells and overall eye health underscores the importance of stem cell therapies in modern ophthalmology. By focusing on regenerative approaches like CALEC, medical professionals can provide innovative solutions that not only heal but also rehabilitate patients’ vision. Continuous research into the biology of these cells will enhance our understanding of corneal repair mechanisms, paving the way for even more effective treatment modalities.
Exploring the Broader Implications of CALEC Surgery
Beyond its immediate application, CALEC surgery has broader implications for the field of regenerative medicine. The success of this stem cell therapy serves as a model for similar approaches in treating other forms of tissue damage throughout the body. By leveraging the principles underlying CALEC, researchers can explore new pathways for addressing diverse medical challenges, ranging from orthopedic injuries to chronic diseases.
Moreover, the collaboration between institutions and the harmonization of clinical trials set a precedent for future research endeavors within multiple specialties. The interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation and encourages the sharing of best practices, ultimately leading to a more significant cumulative impact on patient care. As we advance through this exciting era of medical discovery, CALEC surgery stands out as a beacon of hope for not only vision restoration but for the potential it holds in transforming healthcare as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC surgery and how does it help with corneal restoration?
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell surgery, is a groundbreaking procedure that treats blinding cornea injuries by transplanting stem cells from a healthy eye to a damaged eye. This technique helps restore the cornea’s surface, significantly improving vision and quality of life for patients suffering from severe cornea damage.
How do CALEC stem cell therapy and cornea damage treatment work?
CALEC stem cell therapy involves extracting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye, expanding these cells in a lab to create a graft, and then transplanting the graft into the damaged eye. This method is effective in treating cornea damage that previously was deemed untreatable and has shown a high success rate in restoring corneal function.
What conditions can CALEC surgery effectively treat?
CALEC surgery is primarily designed to treat conditions that lead to limbal stem cell deficiency, including chemical burns, infections, or other eye injuries that result in cornea damage. This innovative approach helps rebuild the cornea’s surface, allowing patients to regain vision and alleviate pain.
Is CALEC surgery safe, and what are its success rates?
CALEC surgery has shown a high safety profile in clinical trials, with no serious adverse events reported. Success rates indicate that over 90% of patients experience significant corneal restoration within months after treatment, showcasing CALEC as an effective option for cornea damage treatment.
What are the eligibility criteria for patients interested in CALEC surgery?
To qualify for CALEC surgery, patients must have at least one healthy eye from which limbal epithelial cells can be harvested. This requirement ensures that the stem cells can be sourced effectively, making it crucial for candidates to have only one affected eye to proceed with the procedure.
Are there any future plans for improving CALEC surgery availability?
Researchers, including those at Mass Eye and Ear, are exploring an allogeneic approach to CALEC surgery, which would utilize limbal stem cells from cadaveric donor eyes. This advancement aims to expand treatment eligibility to patients with damage in both eyes, increasing the overall accessibility of the therapy.
How long does the CALEC procedure take from start to finish?
The entire CALEC procedure spans several weeks, beginning with the biopsy to extract limbal epithelial cells, followed by a two to three-week process to expand these cells into a graft. After sufficient preparation, the surgical transplant can be performed to restore the cornea’s surface.
What role does the cornea play in vision and why is CALEC surgery important?
The cornea is critical for focusing light into the eye; a healthy, intact cornea is essential for clear vision. CALEC surgery is important because it offers a potential solution for patients with severe cornea damage that was previously thought to be irreparable, helping them regain visual function and significantly improve their quality of life.
What differentiates CALEC surgery from traditional corneal transplantation?
Unlike traditional corneal transplantation, which involves replacing the damaged cornea with a donor cornea, CALEC surgery uses the patient’s own limbal epithelial cells to regenerate the cornea. This personalized approach minimizes the risk of rejection and complications associated with donor tissue.
What should patients expect during recovery after CALEC surgery?
Patients undergoing CALEC surgery can expect a careful monitoring process post-surgery to assess the healing of the cornea. Most experience varying improvements in vision and may need to manage minor adverse events, but serious complications are rare, allowing for a generally favorable recovery trajectory.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Procedure Overview | CALEC surgery involves using stem cells from a healthy eye to repair damage in a affected eye, restoring the cornea’s surface. |
| Clinical Trial Success | The trial showed over 90% effectiveness in restoring corneal surfaces after 18 months. |
| Patient Guidelines | Patients must have only one affected eye to undergo the biopsy to obtain limbal stem cells. |
| Safety Profile | The CALEC procedure had a high safety profile with very few adverse events. |
| Future Directions | Researchers are exploring allogeneic manufacturing to treat patients with damage in both eyes. |
Summary
CALEC surgery presents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of ophthalmology, offering new hope to patients with previously untreatable corneal damage. With a remarkable success rate and a high safety profile demonstrated in clinical trials, CALEC surgery utilizes stem cells to regenerate the corneal surface. As this innovative approach continues to evolve, there are aspirations for broader accessibility and effectiveness, paving the way for enhanced vision rehabilitation in individuals afflicted with corneal injuries.