Maternal mortality in the U.S. has alarmingly reached unprecedented heights, making it the highest among wealthy nations. Recent studies reveal that over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, underscoring the urgent need for improving maternal health. A significant rise in these deaths between 2018 and 2022 highlights existing racial disparities in maternal mortality, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest risks. These high maternal mortality rates are compounded by inadequate prenatal and postpartum care, particularly in marginalized communities. As we confront this public health crisis, it is pivotal to address these preventable pregnancy deaths through comprehensive policy reforms that ensure equitable healthcare access for all mothers.
The issue of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States has emerged as a critical public health concern, reflecting alarming trends in reproductive health. A growing body of research indicates that these fatalities, often preventable, highlight significant gaps in care during and after pregnancy. The stark racial disparities in maternal mortality underscore the urgent need for systemic changes to maternity and postpartum support. As the healthcare landscape evolves, focusing on enhancing entitlements to quality care can play a pivotal role in safeguarding maternal lives. By recognizing the necessity for improved health infrastructures and accessible support systems, we can work towards mitigating the risks associated with childbirth and postpartum care.
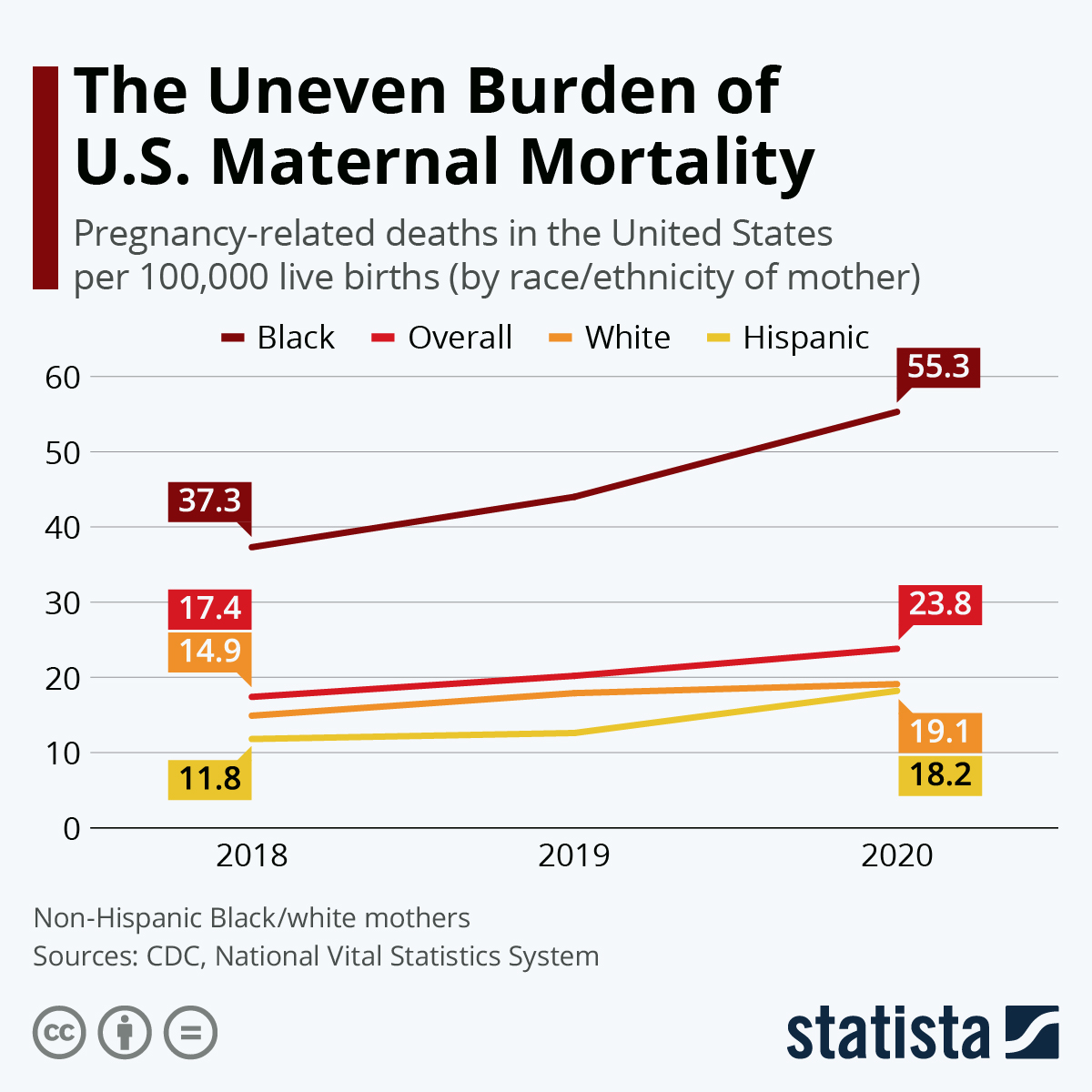
Rising Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
The U.S. continues to lead high-income countries with its rising maternal mortality rates, highlighting a serious public health crisis. Recent studies indicate that maternal deaths have surged, with over 80% of these deaths classified as preventable. Between 2018 and 2022, the rate of pregnancy-related deaths escalated significantly, a trend that reflects systemic issues within the U.S. healthcare system. These findings underscore the necessity for comprehensive reforms in prenatal and postpartum care.
Furthermore, disparities in maternal mortality rates reveal profound racial inequalities. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face nearly four times the risk of mortality compared to their white counterparts. To combat this alarming trend, there is a critical need for targeted policies that address these racial disparities and ensure equitable access to maternal health care across all demographics.
Understanding Preventable Pregnancy Deaths
Despite significant advancements in medical technology and healthcare, preventable pregnancy deaths remain a tragedy within the U.S. healthcare landscape. The leading causes of maternal mortality have transitioned from hemorrhage to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, largely exacerbated by existing health disparities. This shift highlights the pressing need for healthcare providers to prioritize the management of chronic conditions during pregnancy as part of a comprehensive maternal health strategy.
Addressing preventable pregnancy deaths requires a multi-faceted approach, including universal access to high-quality prenatal care and postpartum services. Strategies should focus on education for healthcare providers about risks associated with chronic conditions and the implementation of effective postsurgical care procedures. By implementing such measures, the incidence of maternal deaths could see a significant decline.
Improving Maternal Health Systems
To improve maternal health outcomes, it is essential to invest in robust health systems designed to cater to the needs of pregnant individuals. This includes enhancing access to prenatal care, providing continuous support during the postpartum period, and implementing systemic changes to emergency care in hospitals. Furthermore, a concerted effort to standardize maternity care protocols can bridge the gap in health disparities noted in various states.
Creating a cohesive maternal health strategy involves collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community leaders. By pooling resources and data, stakeholders can better understand the unique challenges faced by various populations, particularly marginalized racial groups disproportionately affected by higher mortality rates. Such collaboration is vital in transforming maternal health care into a more equitable system for all.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Mortality
Racial disparities in maternal mortality are a pressing issue that warrants immediate attention. Data show that non-Hispanic Black women and American Indian women face disproportionately high rates of pregnancy-related deaths compared to their white counterparts. These alarming statistics reveal deep-seated inequities rooted in both systemic bias and a lack of access to quality healthcare.
Efforts to reduce these disparities must focus on expanding access to culturally competent care and increasing investment in health education within underserved communities. Moreover, enhancing accountability within the healthcare system is vital for ensuring that all women receive equitable treatment and support throughout their reproductive health journey.
The Importance of Postpartum Care
Postpartum care is crucial yet often overlooked in maternal health discussions. Notably, nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur in the year following childbirth, indicating a need for comprehensive postpartum support that extends beyond the traditional six-week check-up. Improving postpartum care can significantly reduce the risk of late maternal deaths by addressing potential health issues that may arise during this transitional period.
Healthcare providers must adopt a holistic approach to postpartum care that includes mental health support, chronic disease management, and educational resources for new mothers. By fostering a continuum of care that recognizes the ongoing needs of mothers, we can help ensure that they not only survive childbirth but thrive in their postpartum journey.
Innovative Solutions for Maternal Health
Innovative solutions are essential for addressing the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. One approach includes leveraging technology to improve maternal health monitoring and education, which can empower pregnant individuals to recognize warning signs and access timely care. Additionally, integrating telehealth services can enhance access to medical professionals for those in rural or underserved areas.
Policy changes that facilitate funding for maternal health innovations and health equity programs are critical in the fight against preventable pregnancy deaths. Enhancing research capabilities and creating grants for community-based maternal health initiatives can lead to meaningful improvements in maternal care delivery systems.
Cardiovascular Disease and Maternal Health
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality in the U.S. Understanding this connection and addressing the pre-existing health conditions that contribute to it is vital. Pregnant women face increased risks from issues such as hypertension and gestational diabetes, necessitating continuous monitoring and management of cardiovascular health throughout pregnancy.
Collaborative care models involving obstetricians, cardiologists, and primary care providers are essential for mitigating the risks associated with cardiovascular disease during pregnancy. By enabling early intervention and tailored care plans, healthcare providers can significantly reduce the incidence of maternal deaths related to heart health complications.
Tracking Maternal Deaths Effectively
Effective tracking of maternal deaths is integral to understanding and ultimately reducing maternal mortality rates. The implementation of standardized reporting systems across states has become necessary to ensure accurate data collection concerning pregnancy-related deaths. This step is crucial for identifying trends and developing targeted interventions that can directly influence health policy and healthcare delivery.
With improved data collection mechanisms, public health officials and researchers can gain insights into the multifactorial causes of maternal mortality, leading to more tailored policy responses. Greater accuracy in tracking maternal deaths can enable the development of research initiatives focused on preventive measures and maternal health education.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure
Investing in public health infrastructure is paramount to reversing the troubling trend of rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. As the study indicates, without adequate funding and resources, efforts to improve maternal health outcomes are severely hampered. Public health initiatives must focus on enhancing the capacity of healthcare systems to provide comprehensive and high-quality care to pregnant individuals.
Policy adjustments aimed at securing long-term funding for maternal health programs are crucial. Expanding the scope of services available to women and focusing on preventive care and early intervention can significantly improve health outcomes and save lives.
The Role of Community and Advocacy
Community engagement and advocacy are vital components of improving maternal health outcomes. Local organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness about maternal mortality and empowering women with the knowledge and resources needed to navigate their pregnancy journey. Grassroots movements can help amplify the voices of those most affected by maternal health inequities, driving change at local and national levels.
Furthermore, collaboration with healthcare providers, policymakers, and community members can foster an inclusive approach to maternal health that prioritizes the unique needs of diverse populations. By creating a supportive network that champions maternal health initiatives, we can work toward eliminating the disparities that exist within the healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is at an alarming high, with rates continuing to rise among high-income countries. The rate increased from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births from 2018 to 2022, indicating a rising trend in preventable pregnancy deaths.
What factors contribute to high maternal mortality in the U.S.?
High maternal mortality in the U.S. is attributed to various factors including a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable healthcare policies, and the presence of maternity care deserts. These issues are compounded by chronic health conditions like cardiovascular disease, particularly among younger, reproductive-age populations.
How do racial disparities affect maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Racial disparities in maternal mortality are significant in the U.S. American Indian and Alaska Native women experience a mortality rate nearly four times higher than white women. This highlights the systemic biases and inequities that persist in maternal healthcare.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is crucial in improving maternal health as nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur during the postpartum period, which extends beyond the traditional 42-day window. Adequate postpartum healthcare can help address emerging health issues and reduce late maternal deaths.
Can maternal mortality rates be improved in the U.S.?
Yes, improving maternal mortality rates in the U.S. requires significant investment in public health infrastructure, innovative solutions for pregnancy care, and addressing state-level policy discrepancies. There’s a pressing need for continued focus on both prenatal and extended postpartum healthcare to reduce preventable pregnancy deaths.
What are the leading causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of maternal mortality in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of deaths. Conditions such as hypertension and pre-eclampsia are increasingly affecting younger populations, necessitating better healthcare strategies.
How does the COVID-19 pandemic impact maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic has likely contributed to rising maternal mortality rates, with the sharpest increase occurring in 2021. The pandemic has underscored existing healthcare system vulnerabilities and the need for improved maternal health policies.
Why is it important to consider late maternal deaths in maternal mortality statistics?
Including late maternal deaths—deaths occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum—in statistics provides a more comprehensive understanding of maternal mortality. This recognition emphasizes the need for continuous care in the postpartum period to improve long-term maternal health outcomes.
What measures can be taken to reduce preventable pregnancy deaths?
To reduce preventable pregnancy deaths, it is essential to enhance healthcare access, address systemic inequities, and strengthen public health policies. Promoting quality care during both pregnancy and the postpartum period can significantly improve maternal health outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with significant disparities by state, race, and ethnicity. |
| Increase in Death Rates | From 2018 to 2022, maternal mortality rates increased from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause, accounting for over 20% of deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum. |
| Need for System Improvements | There is a critical need to improve public health infrastructure and provide better healthcare during the postpartum period. |
| Variability Across States | Maternal mortality rates vary significantly from state to state, indicating a need for policy changes. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. remains a growing concern, with rates continuing to rise alarmingly. A recent study highlighted that in the period between 2018 and 2022, the country not only holds the highest rate among high-income nations but also shows marked disparities across racial and state lines. Addressing this challenge requires urgent investment in healthcare infrastructure, particularly around prenatal and postpartum care, to ensure that the majority of preventable deaths can be avoided, ultimately saving lives.